Ongoing projects
The role of domestic companies in the reindustrialisation of the national economy

Principal investigator: Prof. Dr. József Vörös

Source: freepik
As our previous project entitled ’increasing the role of domestic companies in the process of reindustrialising the country’ has proved to be successful, this proposal is a continuation of the previous one. Reindustrialisation is a prevailing topic and by the end of the previous phase we had doubled the number of publications in the first class (Q1) professional journals. Our young colleagues have attended post-graduate courses in excellent institutions like Harvard Business School, MIT Sloan Management School, London School of Economics, and by a contract with HBS we are able to provide the best teaching material for our students for years. So, it seems to be reasonable to base the foundations of the new project on these pillars: we will continue enrolling our young colleagues to best universities, extend the usage of demanding teaching materials, and prevail our enhanced research activity.
At the same time, the accelerated changes due to pandemic, the development of artificial intelligence/digitalisation, and environmental changes draw boarder line between the previous phase and the new one as these events have been causing so dramatic changes that must be considered in all research tracks. To mention some research tracks:
- The pandemic has increased or decreased the role of industrial activities in economic growth.?
- Producing primary information by using questionnaires and running experiments on the personality characteristics and decision-making and thinking styles leading to productive entrepreneurship in a dynamic economic environment involving uncertainties.
- Study how laypeople and professionals make complex financial/consumption decisions, observe the applied information search processes and the considered information cues to formally describe information search and decision-making strategies that may lead to good financial/consumption decisions in the novel digital environments.
- Research focusing on clean production, ESG (Environmental, Societal, Governance) and circular economy issues, investigates the impact of these new considerations on evaluating the pure value of production activities, on the pure financial performance and the judgement of companies by financial markets (stock exchange).
Examining the competitiveness of Hungarian small businesses

Principal investigator: Prof. Dr. László Szerb
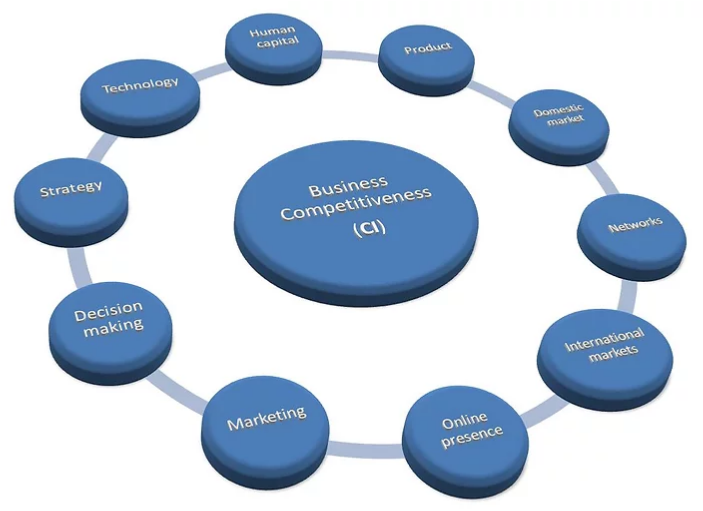
Source: Own editing*
While small units constitute the vast majority of the business sector, our knowledge about the small and medium-sized businesses is limited. To close the gap in small business research, we have developed a unique questionnaire that is a useful tool to measure small business competitiveness. Up to now, we have collected data on 1200 Hungarian and 700 other country businesses. We plan to continue this data collection in 2021 and 2023. The small business competitiveness index consists of ten pillars -human capital, product, domestic market, networks, technology, decision-making, strategy, marketing, internationalisation, and online presence – representing ten features of small business operation. In this project, we would like to examine five important aspects of competitiveness. By analyzing the composition of these pillars, we could provide useful suggestions on small business stakeholders on how to improve the competitiveness of their business. By collecting additional data about the environment of SMEs, we are able to provide useful policy suggestions to local policymakers on how to improve the institutional, local business atmosphere. We are also planning to shed light on the connection between competitiveness and business financial performance. Small businesses export intensity is much lower than large firms, so we aim to identify the key factors of internationalisation and export. Finally, we would like to develop new complex performance measures for family businesses that are more appropriate to quantity family business characteristics and compare them to other nonfamily types of ventures.
* Read the full paper: Lafuente, E. et al. (2019) BRQ Business Research Quarterly, DOI: 10.1016/j.brq.2019.02.002 here.
With resilient systems against climate change

Principal investigator: Dr. Tibor Kiss
Source: kekgazdasag.hu
The question beyond the research is what are the main features of the production systems, which are considered as the most advanced sustainable systems of our age? The research demonstrates examples of resilient micro-regional economic systems, which fulfil the requirements of the blue and the circular economy.
- Mushroom production in Belgrad (Serbia): An ecological innovative production model for mushroom production.
- Energy production in El Hierro (Spain): El Hierro can be a worldwide benchmark island in implementing energy self-sufficiency and autonomy systems.
- DYCLE (Diaper Cycle, Berlin) – production circle around a totally recyclable diaper: it is converted into black soil, which is used for growing fruit trees and fruits are converted to baby food and juice.
- N17 Brewery (Galway, Ireland) – a beer factory by blue economy principles. This factory produces more than eight products, including mushrooms, dog biscuits, fish.
These cases will be fully processed with the following outputs:
- A system dynamics (or the appropriate) model to cover the general framework of the case;
- Calculation of the Fitness of Evaluation indicator (for the resilience of the system);
- The popular Business Generator Canvas is further developed for a blue canvas. Each model will be demonstrated by this canvas.
- A detailed Hungarian language documentation for further usage.
The project aims to publish 112 blue business cases and clusters in Hungarian language online. The research results are continuously published on the theblueeconomy.hu page.
Development of hydrogen-based, resilient city-region protocol and IoT monitoring system for economic development

Principal investigator: Dr. Zsolt Bedő
Source: freepik
The increasing frequency of global shocks requires continuous adaptation from economic actors, irrespective of them being individuals, companies or settlements. Resilience as a skill has gained value as this characteristic ensures the responsiveness of an economic unit in face of a shock related to energetics, natural resource, raw material or any kind of other input factors. Many new solutions, technologies emerge that try to solve this issue, however the quick implementation of one single new technology does not necessarily lead to the expected changes if the economic and social embedding of the given technology is not adequate. The same is true for the widely cited hydrogen technology today. If the company or settlement choosing the costly hydrogen technology does not fit it into existing value chains and production processes, then its social and economic impact will be suboptimal.
Ongoing research at the UPFBE addresses this current problem through developing a protocol with the help of which experts are able to formulate advices with respect to moving towards hydrogen-based operations at the city-region or company levels. This includes the ’circular’ way of thinking as well if it is relevant in the given situation.
Beyond formulating advices, the research develops an IoT framework which can be used to monitor resilience at the level of the unit deciding to use hydrogen-based technology. With this framework, the unit is able to continuously measure the impact of technological and economic interventions and prove its the ESG development towards potential financing agencies and authorities which is closely related to the original goal, that is resilience.
Vulnerability, specialisation and development pathways in global value chains

Principal investigator: Dr. Tamás Sebestyén
Source: own editing
Globalization and economic integration have reshaped production and trade, creating complex global value chains. While these complex value chains have contributed to efficiency and national incomes, they have also increased the interdependence and vulnerability of economies. Transition economies, particularly in Central and Eastern Europe, face unique challenges in this landscape. They often integrate into global value chains at lower value-added stages, leading to economic duality where advanced, foreign-owned sectors coexist with less productive domestic sectors. This dual economic structure exacerbates vulnerabilities and hinders upward mobility within global value chains. Addressing this duality and understanding the pathways to higher value-added production is therefore critical to enhancing economic stability and development in these regions.
The research develops diagnostic tools that capture the divide between foreign-owned and domestic firms. This helps to understand the nature and drivers of this specific economic structure and to identify possible development paths within global value chains. It also seeks to understand how economic resilience can be built together with a shift towards higher value-added economic activities. The research provides a comprehensive understanding of the dual economic structure and its implications for development and resilience. By identifying successful development pathways and the conditions that enhance resilience, the project will provide valuable guidance to policymakers navigating the complexities of globalization and economic integration.
The research team and results can be followed on the EconNet webpage.
The role of motivated reasoning and effectuation entrepreneurship in entrepreneurial behaviour and innovation (4-year research project, ID: 147233 "OTKA" K_23 grant)

Principal investigator: Prof. Dr. Zsófia Vörös

Source: freepik
Entrepreneurship makes a significant contribution to inclusive economic growth, social, technological and economic innovation. However, little is known about how entrepreneurial decisions are made in an uncertain environment and the mechanisms through which certain entrepreneurial decisions lead to success and innovation. The proposed project aims to contribute to research on this topic.
Entrepreneurial behaviour is often seen as the result of decisions made in an uncertain and dynamic environment, based on subjective value judgements. The entrepreneurial life course thus unfolds in an environment where the utility of all possible alternatives for action cannot be assessed at the moment of decision, and thus utility maximisation based on neoclassical rational decision logic is not feasible.
Within the first research phase of the project, we therefore aim to operationalise entrepreneurial effectuation along the lines of general decision-making theories and link it to entrepreneurial innovation and success. The logic of entrepreneurial effectuation, by reversing the cause and effect relationships of profit-maximising decisions, takes the tools available in the hands of the entrepreneur at the moment of the decision and uses them to achieve new and acceptable goals according to the aspirational level of the decision-makers.
However, some recent studies have shown that many business decisions are made under high levels of uncertainty, where environmental information signals provide no guidance at all for assessing the outcome of possible behaviours at the time of the decision. For example, when making decisions that lead to market entry or radical innovation, entrepreneurs lack information and experience about the situations that may result from their decisions. In the absence of clear environmental cues, heuristics may not be an effective decision-making mechanism, and researchers on this topic have proposed motivated reasoning as an argument that enables entrepreneurial behaviour in such cases. Therefore, in the second phase of the project, we plan to run experiments that investigate the role of motivated thinking in entrepreneurial strategic decisions.
In summary, we want to generate new knowledge about entrepreneurial decision logics and their role in success and innovation.
The chances and opportunities for the development of smart destinations and smart tourism in Hungary with special regard to the challenges of the post-pandemic period („OTKA” K_22 application, NKFI N 142571 identification number, 4 years of research)

Principal investigator: Dr. János Csapó

Source: freepik
Smart tourism is one of the newest and most innovative trends in tourism development of our time, the development of which has already started in many places abroad – even in internationally prominent tourist destinations – but its development and embeddedness in Hungary can only be found at the level of mention. One of the pillars of this can of course be detected in the initial works of domestic researchers. The other main direction is the start of the development of data-driven tourism and sector management, which is also recognised by the Hungarian Tourism Agency in 2021. Within this framework, from November 2021, the tourist accommodation and tourist attractions will be channelled to the so-called National Tourism Data Service Centre (NTAC) (Nemzeti Turisztikai Adatszolgáltató Központhoz, NTAK), which will provide Hungary's most comprehensive, real-time big data to support the Agency's work and the development of Hungarian tourism. The research of this database will also open up many new opportunities for background analyses of Hungarian tourism.
In our opinion, as the ultimate goal of smart tourism is to improve the efficiency of resource management, increase digitalisation (in which Hungary’s tourism is lagging behind), maximise competitiveness and enhance sustainability through the application of technological innovations and practices, the importance and value of research in this area concerning the innovative development of tourism is unquestionable and fully in line with EU tourism policy as well.
The overall research aim is to explore the chances and opportunities for the development of smart tourism in Hungary and in the tourist destinations of Hungary. The main questions of our research are:
- RQ1: Can smart tourism and smart destinations be developed in our country, and if so, how and in what form?
- RQ2: What role can smart tourism and the development of smart destinations play in the re-launch and re-design of domestic tourism?
- RQ3: What needs and attitudes can be identified on the consumer side for domestic smart tourism and smart tourism in general?
In the course of our research, we have identified the following objectives and expected results, which we believe have both theoretical and practical value and novel outcomes:
- Explore the theoretical foundations and the international and national research background of smart tourism through a systematic literature review.
- A complex exploration of the theoretical and practical background and application possibilities of smart tourism, exploring international models, identifying and presenting good practices, taking into account the results of the EU's Smart Tourism Communities programme.
- Developing and providing methodological basis for the development of smart tourism strategies at destination level, especially in the 11 tourist areas defined by the Hungarian Tourism Agency.
- Developing and providing methodological and practical bases for the introduction and dissemination of smart tourism at enterprise and entrepreneurial level, in particular by strengthening networking.
A representative survey of consumer attitudes towards smart tourism.
Dynamic Model Of The Relationship Of Optimized Customer Behaviour And Firm Performance In The Changing Omnichannel Purchasing Environment (OTKA 146356, 2024-2026)

Principal investigators: Dr. Krisztián Szűcs (UP), Prof. Dr. Simon Judit (CUB)

Source: freepik
The development of omnichannel shopping behaviour as a dynamic process is still under-researched topic in international literature. There are only a few research results on the Hungarian omnichannel buying behaviour as well, and only a few research has previously focused on customer behaviour in this environment, although this is a relevant and important area not only for the scientific research but for the companies as well.
The first and maybe the most important result of our research is to get to know better the optimized decision-making process of consumers in omnichannel environment, and to give an empirically tested review about the omnichannel behavioural patterns. With our research, we would like to develop a measuring method, a scale of omnichannel behavioural intention. This scale is not only useful for the academic researchers but also significant and important for the managers and companies connected to omnichannel retailing. Using this scale, they will be able to get to know their consumers better and to plan better omnichannel services. According to this result, their services and e-commerce activities could be developed for achieving higher satisfaction and loyalty, which are key dimensions of performance.
Our secondary aim is to give a thorough understanding of the omnichannel behaviour from the aspect of COVID19, and to show whether the behaviours have been changed between 2021 and 2024.
Research fellows: Dr. Ildikó Kemény (CUB), Dr. Zombor Berezvai (CUB), Dr. Ákos Nagy (UP)
